Search engines like Google have a problem. It’s called ‘duplicate content.’ Duplicate content means that similar content is being shown on multiple locations (URLs) on the web. As a result, search engines don’t know which URL to show in the search results. This can hurt the ranking of a webpage. Especially when people start linking to all the different versions of the content, the problem becomes bigger. This article will help you to understand the various causes of duplicate content, and to find the solution for each of them.
What is duplicate content?
You can compare duplicate content to being on a crossroad. Road signs are pointing in two different directions for the same final destination: which road should you take? And now, to make it ‘worse’ the final destination is different too, but only ever so slightly. As a reader, you don’t mind: you get the content you came for. A search engine has to pick which one to show in the search results. It, of course, doesn’t want to show the same content twice.
Let’s say your article about ‘keyword x’ appears on https://ift.tt/2HzipT2 and the same content also appears on https://ift.tt/2r7vSWS. This situation is not fictitious: it happens in lots of modern Content Management Systems. Your article has been picked up by several bloggers. Some of them link to the first URL; others link to the second URL. This is when the search engine’s problem shows its real nature: it’s your problem. The duplicate content is your problem because those links are both promoting different URLs. If they were all linking to the same URL, your chance of ranking for ‘keyword x’ would be higher.
Learn how to write awesome and SEO friendly articles in our SEO Copywriting training »
 Info
Info
Table of contents
1 Causes for duplicate content
There are dozens of reasons that cause duplicate content. Most of them are technical: it’s not very often that a human decides to put the same content in two different places without distinguishing the source: it feels unnatural to most of us. The technical reasons are plentiful though. It happens mostly because developers don’t think as a browser or a user, let alone a search engine spider, they think as a developer. That aforementioned article, that appears on https://ift.tt/2HzipT2 and http://www.example.com/article-category/keyword-x/? If you ask the developer, he’ll say it only exists once.
1.1 Misunderstanding the concept of a URL
Has that developer gone mad? No, he’s just speaking a different language. You see a database system probably powers the whole website. In that database, there’s only one article, the website’s software just allows for that same article in the database to be retrieved through several URLs. That’s because, in the eyes of the developer, the unique identifier for that article is the ID that article has in the database, not the URL. For the search engine though, the URL is the unique identifier to a piece of content. If you explain that to a developer, he’ll start getting the problem. And after reading this article, you’ll even be able to provide him with a solution right away.
1.2 Session IDs
You often want to keep track of your visitors and make it possible, for instance, to store items they want to buy in a shopping cart. To do that, you need to give them a ‘session.’ A session is a brief history of what the visitor did on your site and can contain things like the items in their shopping cart. To maintain that session as a visitor clicks from one page to another, the unique identifier for that session, the so-called Session ID, needs to be stored somewhere. The most common solution is to do that with cookies. However, search engines usually don’t store cookies.
At that point, some systems fall back to using Session IDs in the URL. This means that every internal link on the website gets that Session ID appended to the URL, and because that Session ID is unique to that session, it creates a new URL, and thus duplicate content.
1.3 URL parameters used for tracking and sorting
Another cause for duplicate content is the use of URL parameters that do not change the content of a page, for instance in tracking links. You see, https://ift.tt/2HzipT2 and https://ift.tt/1CRUpLZ are not the same URL for a search engine. The latter might allow you to track what source people came from, but it might also make it harder for you to rank well. A very unwanted side effect!
This doesn’t just go for tracking parameters, of course. It goes for every parameter you can add to a URL that doesn’t change the vital piece of content, whether that parameter is for ‘changing the sorting on a set of products’ or for ‘showing another sidebar’: they all cause duplicate content.
1.4 Scrapers & content syndication
Most of the causes for duplicate content are all your own or at the very least your website’s ‘fault.’ Sometimes, however, other websites use your content, with or without your consent. They do not always link to your original article, and thus the search engine doesn’t ‘get’ it and has to deal with yet another version of the same article. The more popular your site becomes, the more scrapers you’ll often have, making this issue bigger and bigger.
1.5 Order of parameters
Optimize your site for search & social media and keep it optimized with Yoast SEO Premium »
 Info
InfoAnother common cause is that a CMS doesn’t use nice and clean URLs, but rather URLs like /?id=1&cat=2, where ID refers to the article and cat refers to the category. The URL /?cat=2&id=1 will render the same results in most website systems, but they’re completely different for a search engine. 1.6 Comment pagination
In my beloved WordPress, but also in some other systems, there is an option to paginate your comments. This leads to the content being duplicated across the article URL, and the article URL + /comment-page-1/, /comment-page-2/ etc.
1.7 Printer friendly pages
If your content management system creates printer friendly pages and you link to those from your article pages, in most cases Google will find those, unless you specifically block them. Now, which version should Google show? The one laden with ads and peripheral content, or the one with just your article?
1.8 WWW vs. non-WWW
One of the oldest in the book, but sometimes search engines still get it wrong: WWW vs. non-WWW duplicate content, when both versions of your site are accessible. A less common situation but one I’ve seen as well: HTTP vs. HTTPS duplicate content, where the same content is served out over both.
2 Conceptual solution: a ‘canonical’ URL
As determined above, the fact that several URLs lead to the same content is a problem, but it can be solved. A human working at a publication will normally be able to tell you quite easily what the ‘correct’ URL for a certain article should be. The funny thing is, though, sometimes when you ask three people in the same company, they’ll give three different answers…
That’s a problem that needs solving in those cases because, in the end, there can be only one (URL). That ‘correct’ URL for a piece of content has been dubbed the Canonical URL by the search engines.
Ironic side note
Canonical is a term stemming from the Roman Catholic tradition, where a list of sacred books was created and accepted as genuine. They were dubbed the canonical Gospels of the New Testament. The irony is: it took the Roman Catholic church about 300 years and numerous fights to come up with that canonical list, and they eventually chose four versions of the same story…
3 Identifying duplicate contents issues
You might not know whether you have a duplicate content issue on your site or with your content. Let me give you some methods of finding out whether you do.
3.1 Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a great tool for identifying duplicate content. If you go into the Search Console for your site, check under Search Appearance » HTML Improvements, and you’ll see this:
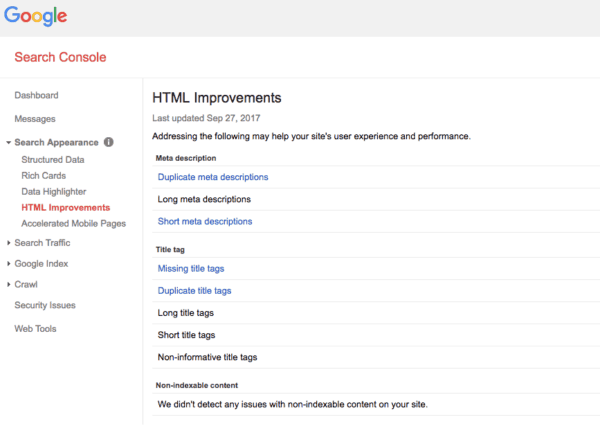
If pages have duplicate titles or duplicate descriptions, that’s almost never a good thing. Clicking on it will reveal the URLs that have duplicate titles or descriptions and will help you identify the problem. The issue is that if you have an article like the one about keyword X, and it shows up in two categories, the titles might be different. They might, for instance, be ‘Keyword X – Category X – Example Site’ and ‘Keyword X – Category Y – Example Site’. Google won’t pick those up as duplicate titles, but you can find them by searching.
3.2 Searching for titles or snippets
There are several search operators that are very helpful for cases like these. If you’d want to find all the URLs on your site that contain your keyword X article, you’d type the following search phrase into Google:
site:example.com intitle:"Keyword X"
Google will then show you all pages on example.com that contain that keyword. The more specific you make that intitle part, the easier it is to weed out duplicate content. You can use the same method to identify duplicate content across the web. Let’s say the full title of your article was ‘Keyword X – why it is awesome’, you’d search for:
intitle:"Keyword X - why it is awesome"
And Google would give you all sites that match that title. Sometimes it’s worth even searching for one or two complete sentences from your article, as some scrapers might change the title. In some cases, when you do a search like that, Google might show a notice like this on the last page of results:

This is a sign that Google is already ‘de-duping’ the results. It’s still not good, so it’s worth clicking the link and looking at all the other results to see whether you can fix some of those.
4 Practical solutions for duplicate content
Once you’ve decided which URL is the canonical URL for your piece of content, you have to start a process of canonicalization (yeah I know, try to say that three times out loud fast). This means we have to let the search engine know about the canonical version of a page and let it find it ASAP. There are four methods of solving the problem, in order of preference:
- Not creating duplicate content
- Redirecting duplicate content to the canonical URL
- Adding a canonical link element to the duplicate page
- Adding an HTML link from the duplicate page to the canonical page
4.1 Avoiding duplicate content
Some of the above causes for duplicate content have very simple fixes to them:
- Session ID’s in your URLs?
These can often just be disabled in your system’s settings.
- Have duplicate printer friendly pages?
These are completely unnecessary: you should just use a print style sheet.
- Using comment pagination in WordPress?
You should just disable this feature (under settings » discussion) on 99% of sites.
- Parameters in a different order?
Tell your programmer to build a script to always order parameters in the same order (this is often referred to as a so-called URL factory).
- Tracking links issues?
In most cases, you can use hash tag based campaign tracking instead of parameter-based campaign tracking.
- WWW vs. non-WWW issues?
Pick one and stick with it by redirecting the one to the other. You can also set a preference in Google Webmaster Tools, but you’ll have to claim both versions of the domain name.
If you can’t fix your problem that easily, it might still be worth it to put in the effort. The goal would be to prevent the duplicate content from appearing altogether. It’s by far the best solution to the problem.
4.2 301 Redirecting duplicate content
In some cases, it’s impossible to entirely prevent the system you’re using from creating wrong URLs for content, but sometimes it is possible to redirect them. If this isn’t logical to you (which I can understand), do keep it in mind while talking to your developers. If you do get rid of some of the duplicate content issues, make sure that you redirect all the old duplicate content URLs to the proper canonical URLs.
Learn how to write awesome and SEO friendly articles in our SEO Copywriting training »
 Info
Info 4.3 Using rel=”canonical” links
Sometimes you don’t want to or can’t get rid of a duplicate version of an article, even when you do know that it’s the wrong URL. For that particular issue, the search engines have introduced the canonical link element. It’s placed in the section of your site, and it looks like this:
<link rel="canonical" href="http://example.com/wordpress/seo-plugin/">
In the href section of the canonical link, you place the correct canonical URL for your article. When a search engine that supports canonical finds this link element, it performs what is a soft 301 redirect. It transfers most of the link value gathered by that page to your canonical page.
This process is a bit slower than the 301 redirect though, so if you can do a 301 redirect that would be preferable, as mentioned by Google’s John Mueller.
Read more: ‘ rel=canonical • What it is and how (not) to use it ’ »
4.4 Linking back to the original content
If you can’t do any of the above, possibly because you don’t control thesection of the site your content appears on, adding a link back to the original article on top of or below the article is always a good idea. This might be something you want to do in your RSS feed: add a link back to the article in it. Some scrapers will filter that link out, but some others might leave it in. If Google encounters several links pointing to your article, it will figure out soon enough that that’s the actual canonical version of the article.
5 Conclusion: duplicate content is fixable, and should be fixed
Duplicate content happens everywhere. I have yet to encounter a site of more than 1,000 pages that hasn’t got at least a tiny duplicate content problem. It’s something you need to keep an eye on at all times. It is fixable though, and the rewards can be plentiful. Your quality content might soar in the rankings by just getting rid of duplicate content on your site!
Keep reading: ‘ Ask Yoast: webshops and duplicate content’ »
https://ift.tt/1G5ik3j